Introduction
Performing a regular SEO eCommerce site audit should be part of your online marketing strategy (if it isn’t already).
As an eCommerce business that wants to have a steady growth, your website is a paramount touchpoint in your customers’ journey, as well as the prime source of conversions and, ultimately, revenue. If you don’t have a physical presence, then your online store is even more important.
Optimizing it according to the best practices of your vertical and rising customer expectations is, of course, a good start. But apart from industry trends and customer insights, there is one more variable that should dictate how you define and further optimize your website: search engines.
To deliver the most relevant search results to users’ queries, search engines use algorithms that consist of multiple ranking factors. These algorithms are constantly changed and updated, but most of those updates won’t be that significant in scope to require a complete makeover of your website.
However, you will still want to optimize your eCommerce site regularly to maintain its relevancy within the ever-changing algorithms, and an SEO website audit is a good starting point in this process.
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO eCommerce audit involves evaluating the current performance and health of your entire eCommerce website, and accomplishes the following:
- Identifies SEO issues that are currently impacting the performance of your website
- Suggests optimizations for improved performance.
- Contributes directly to the overall increase in website performance, visibility, and organic traffic.
In the end, an SEO eCommerce audit provides guidance for your SEO strategy by illuminating areas you need to improve and how to do so.
Additionally, if SEO is already part of your online marketing strategy, a website audit can help you compare results of your current optimization campaign to past ones. This enables you to better evaluate whether and by how much your SEO efforts are paying off.
If SEO wasn’t a priority until now, the audit will be a good starting point to see where you stand, by providing a snapshot at time t=0 so you have a comparison benchmark when you evaluate results.
A typical SEO audit checklist will cover the following areas:
- Technical SEO – The technical aspects of your website ensure that search engines can crawl and index it. As Moz’s “Hierarchy of SEO Needs” puts it, crawl accessibility is the foundation of any SEO strategy (and therefore technical SEO should be the starting point of your SEO audit);
- On- and off-page analysis – On-page SEO is focused on the page content and HTML elements (these help search engines understand the web page’s relevancy for the search query). On the opposite pole, off-page SEO refers to external links and other signals (branded searches, brand mentions, reviews, etc.) that build on your website’s authority and trustworthiness;
- Content gaps and opportunities – Although content is part of the on-page SEO, it requires a separate section in your audit. As the “Hierarchy of SEO Needs” indicates, content contributes to off-page SEO as well (as it can gain your site credible links, citations, and more). Therefore, content has a two-fold objective – to increase organic traffic and to improve authority;
- User experience – Apart from relevant and qualitative content, search engines aim to provide users with the best overall experience. That’s why they will always prioritize websites that are aligned with the latest UX best practices.

Source: PageTraffic
Why Is an SEO Audit Important for eCommerce Sites?
Search engines are the gatekeepers to organic traffic.
Of course, there are multiple sources of traffic, but no matter what your budget, company size, and experience is, organic traffic should be part of your strategy.
As the statistics show, organic traffic generates significant opportunities for eCommerce businesses:
- With shopping being among the most popular online activities, it is no surprise that eCommerce revenue is projected to reach 54 trillion US dollars by 2022. But the industry is also becoming highly competitive.
- 81% of people search online for products/services. In fact, individuals use search engines every day.
- After referral and paid, organic traffic generates the highest conversion rates;
- 33% of website revenue is generated by organic traffic, recording a 21% YOY growth;
- Organic traffic is long-term. While paid traffic lasts for as long as you pay, organic traffic takes more time to gain traction, but lasts much longer (and is less hard on the budget).
If you’re looking at the overall stats, you’ll see that organic traffic continues to be among the first sources of eCommerce conversions/revenues, coming close to paid traffic. So, SEO is not going anywhere, anytime soon.
In the highly competitive eCommerce industry, it is instrumental that your eCommerce site ranks high in search engine result pages (SERPs).
Now that you have a sense of why SEO is important for eCommerce, let’s dive right into the basic steps of your website audit!
eCommerce SEO Audit Checklist
Here are the main elements that you want to assess in your eCommerce website audit:
1. Technical SEO
As we outlined before, technical SEO is all about making your eCommerce website easy to be crawled, indexed, and ranked by search engine robots.
Crawlability
Search engines use robots (also known as “spiders”) to discover content. To do this, they follow links, and that’s exactly why your website discoverability is heavily influenced by both external and internal links. When accessing your website, the robots analyze its structure to determine its relevancy and ranking in SERPs.
Crawling is the very first step in the ranking process, but you know what they say, “first impressions are the last impressions.” To avoid having search engines reject your website for indexation or rank you low, you want to have a fully optimized setup.
Your SEO audit should start by crawling your eCommerce website. There are several tools that simulate a crawling process, and you can configure them to behave like the search engine you’re interested in (Google, Bing, etc.). They’ll diagnose the technical issues that require your attention.
Let’s see some of the technical aspects that are important in the crawling process:
-
Robots.txt
The Robots.txt file tells search engine robots what they are allowed and disallowed to crawl and index from your website. This file is usually found at:
<code> https://www.domain.com/robots.txt </code>
There will be certain parts of your eCommerce website that you don’t want crawled and indexed (for instance, test pages, thank-you pages, the shopping cart pages, etc.). However, be careful when setting up the Robots.txt file, otherwise you run the risk of preventing search engine robots from finding important areas on your site.
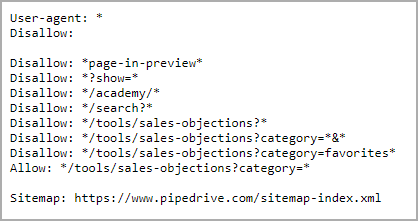
For example, Pipedrive disallowed search engine robots to crawl and index some of its subfolders, including the Academy and Sales Objections sections of its website. Diving even deeper, we can see that Pipedrive instructed search engines to not access the category page “Favorites” from the Sales Objection subfolder.
-
Meta robots
Meta robots are similar to Robots.txt file in the sense that they instruct search engines how to crawl your website. However, meta robots also allow for further directives such as whether to index the page or not, and whether to follow the links it contains.
This is recommended if you have pages that you want to be crawled but not appear in SERPs, or if you don’t want to transfer your domain’s link authority to the included links. Such pages can be those that contain duplicate content (e.g. filter pages).
-
XML Sitemap
An XML map is simply a listing of all the relevant pages in your website.
As we said, the crawling process consists of search bots following links and discovering new content from one link to another. If important pages from your website do not contain any internal links (we’ll talk more about them later), bots may find it hard to find and crawl them.
An XML map will give more structure to your website, preventing search bots from overlooking important parts of it and making the crawling process more efficient.
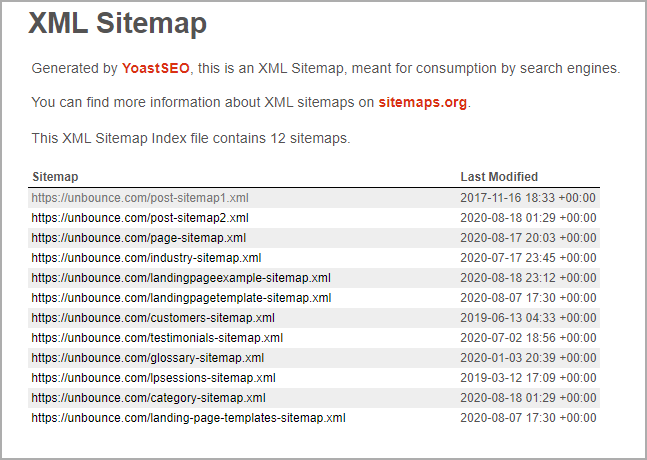
According to Google, very large websites with rich media content benefit most from an XML map. eCommerce websites tend to be particularly extensive due to having many filter pages, category pages, and product pages. They also have rich media content due to product images, videos, and more. As such, a sitemap would be even more helpful in structuring your website for search bots.
Looking at Unbounce’s XML sitemap, we can see that the main file contains 12 sitemaps. Each sitemap then consists of an extensive list of the web pages.
If you don’t already have such a map, it’s time to submit one. If you do, make sure to keep it updated.
Indexation analysis
Once the robots have crawled your website and deemed it relevant, they’ll store its latest HTML version in a large database (also known as the Search index for Google).
It’s important to know that it will take search bots some time to crawl your website again and index the new HTML, following your eCommerce site audit.
When performing SEO audits, the most common indexation issues include:
-
Duplicate content
Duplicate content refers to content that appears on multiple pages, whether from the same domain or across more domains.
Don’t worry, though. Google understands that certain types of duplicate content are non-malicious in nature. However, penalizations will be triggered when duplicate content is created with the sole purpose of manipulating search engines.
We hinted at this before – as an eCommerce business, your website will most likely have filter pages that create the risk of duplicate content. When users have the option to filter products based on variables like type, size, color, etc., your existing content is simply narrowed down, creating multiple instances of the same product content. The same thing can happen with category pages.
Another pitfall is related to product descriptions – simply copying the description provided by the manufacturer automatically signals search bots that they are dealing with duplicate content.
The solution: Canonical Tags
Although search engines do not penalize duplicate content that will emerge naturally (e.g. from filter pages), you still want to avoid any confusion in indexation.
You can solve duplicate content issues by specifying to search engines which URL they should index and rank. Just use the rel=canonical attribute with the original version of the URL you want to appear in SERPs.
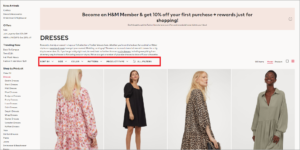
For instance, H&M allows visitors to filter each of their clothing sections (dresses in this example) by size, color, pattern, and type.
To prevent search engines from indexing any of these filter pages, H&M indicated the main page version that should rank in SERPs:
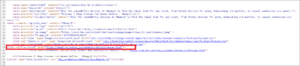
-
Internal links
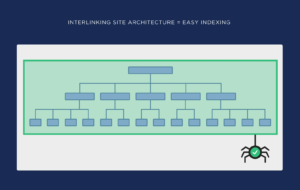
Apart from an XML sitemap, a good internal linking strategy can also prevent crawling issues. If you’re strategically linking to your own pages, search bots will find it easier to navigate your website and identify those important pages.
Organize your internal links so that you build a simple and clear architecture for search engines:
A flatter architecture – fewer clicks from the homepage to the important pages – is preferred as it enables search bots to easily crawl your website.
Of course, a good interlinking strategy also contributes to boosting organic traffic.
But internal links can bring their fair share of indexation issues, as can be seen below.
-
404s
This error appears when a link leads to a non-existing page on your website. Depending on the reason they’re occurring, their impact on your SEO will vary. Overall, it’s ideal to minimize the number of such 404 errors because neither the users nor the search engines fancy them.
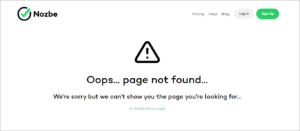
404 error pages can occur for a variety of reasons:
- Broken internal links – these occur because you either intentionally deleted existing pages (for instance, very old pages) from your website or you linked two pages incorrectly (i.e. misspelling the URL). Broken links negatively impact user experience, as well as search bots’ ability to crawl your website.
- Soft 404s – these are pages that no longer exist, but because of some server issues, they return a 200 status code. This indicates that the request of returning the page has succeeded. In terms of SEO impact, soft 404s waste search engines’ crawl budget. Instead of spending time on pages that actually exist, search bots will be crawling and indexing these soft 404s (which they do not identify as real 404s).
There’s no magic secret or tool to prevent this type of error from ever occurring within your website. You need to regularly monitor and fix 404s. The great news is that you can easily retrieve them using Google Search Console, or other tools.
If these pages were already indexed, search engines will simply remove them from the index, so they will not appear in SERPs. This is desirable for those intentionally removed pages.
Finally, to minimize the impact on user experience, you may want to create a custom 404 page.
-
Redirects
There are multiple ways of fixing 404 errors pages generated by broken links. One such way is using a 301 redirect to another relevant page that best serves the user intent, or your homepage.
If a 404-page had reputable backlinks and a lot of traffic, then you don’t want the link authority to be spilled – that’s exactly how a redirect helps.
30x redirects don’t lose PageRank anymore.
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (@methode) July 26, 2016
HTTPS
Another ranking signal is the HTTPS protocol which ensures a secure connection to your website.
Implementing a HTTPS via a SSL certificate will protect the customer’s data (such as login credentials and sensitive information like credit card information). The SSL certificate encrypts the data transferred from the browser to the website’s server, so it cannot be intercepted by hackers.
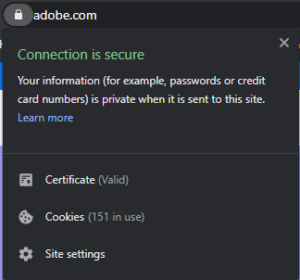
Make sure to check that all your website assets (such as images, video, or scripts) are also hosted on secure URLs.
2. On-page SEO
On-page SEO refers to the HTML elements and content in a web page that can be optimized. All these on-page optimizations should be based on your keyword research.
-
Keyword research
Keyword research will help you gain an understanding about your target audience. Discovering the keywords that they use most often will give you a starting point to design on-page content that caters to their needs.
First, create a list of relevant keywords for your eCommerce business. You surely have some keywords in mind that you would like to rank for, so start by searching those in a keywords research tool (Moz, SEMrush, Ahrefs etc). You’ll get similar, related keywords as well as search volume and difficulty to rank for.
Another thing you can do is manually type a keyword in Google and see what suggestions you get, and also check for the “Searches related to” section or “People also ask.” It’s also useful to research competition.
Second, you need to choose what keywords to target from your list, and there will be several variables you’ll want to look at – search volume, keyword difficulty, even the cost-per-click (CPC). The right figures for search volume and keyword difficulty depend very much on your industry. While striking the right balance between the search volume and competitiveness of a keyword can be challenging, long-tail keywords are key.
Finally, make sure that those targeted keywords match your users’ intent (which, for an eCommerce business will most likely be transactional).
Now that you’ve narrowed down your list, it’s time to incorporate those targeted keywords in your on-page content.
Pro tip – keyword research is not a one-time activity. When you’re doing your SEO audit, make sure to refresh your keyword research as well. In an ever-changing industry like eCommerce, your current targeted keywords may no longer be relevant or new keywords may have emerged.
-
Title tags
Title tags are written in the HTML code and appear when the page is displayed in SERPs, in the browser’s tab title, bookmarks, as well as when users share the link on social media.
SEO best practices advise including the page’s primary keyword in the title tag. For an eCommerce business, it’s also good to include the name of the company.
You want to have a catchy title tag that would convince users to access your web page.
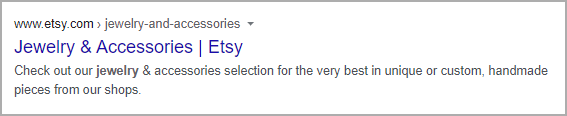
Etsy provides a good example of SEO-friendly title tag. It’s clean and it comprises the brand as well.
-
Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions are essential in maximizing click-through rates (CTR). Although not directly considered a ranking factor, they can influence the organic traffic you get.
On one hand, the users’ searched keywords are highlighted in bold – this can prompt them to click on your web page. Make sure to include your targeted keywords in the description to fully benefit from this feature provided by search engines.
On the other hand, as an eCommerce business, you can include some incentives in the description. If you provide free shipping, discounts, or any other perk, make sure to include them and attract users’ attention.
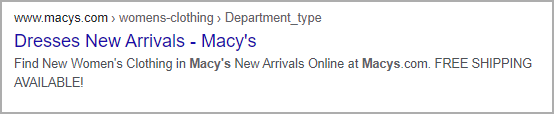
For example, Macy’s used capital letters to emphasize their free shipping option.
-
Headings
Headings are not necessarily a ranking factor either, but they help search engines understand what your content is about. And the better search engines understand your content, the better the ranking you’ll get for relevant queries.
Headings will also help make your content more readable – and we know search engines consider readability as a ranking factor. Readers also like them, because it makes it easier for them to skim though the text and see if they can find what they need on that page.
Make sure you have a single H1 that includes your primary keyword (but be careful, H1 is not the same as the title tag). Then incorporate H2s to H6s to break up large chunks of text.
-
Alternative text
Search engine bots cannot read images, which is why including an alt attribute to them is important.
You can also include your target keyword in the alt text if it indeed adds value and describes what the image is about.
As part of your website audit, you need to ensure that all your images have relevant alt texts.
-
Interlinking
We discussed using internal links in the technical SEO section, but there is one more aspect to them that impacts the on-page SEO.
You should be strategic when you’re doing interlinking. Depending on how you link your pages to one another will signal to search engines which one is more important and will rank it higher. So, link your pages to important ones that you want to rank on the first page in SERP. Usually, these are the ones that target high-volume keywords, and that are of an outstanding quality (i.e. your best content).
Also, make sure your anchor text is the exact or partial match of the targeted keyword of the page you want to link to.
-
Page content (keyword optimization)
Finally, content is the most important part of any web page. All the previous HTML elements contributed to building a SEO-friendly page structure for your cool content.
We’ll talk more about your content later, but for now keep in mind that it’s essential to have it keyword optimized. That’s why you do a keyword research in the first place – to understand your target audience, and to come up with topics that answer their queries.
Bonus: eCommerce-specific pages
There are two types of pages that any eCommerce business will have – product and category pages.
We hinted at this before: optimizing these eCommerce pages might be more challenging than optimizing other types of websites. They have certain features – a high number of products or fluctuating inventory – which can lead to some of the issues mentioned above (crawl budget, duplicate content, or internal linking issues).
-
Product Pages
No matter what product you’re selling, all links in your website should lead to your product pages (because conversion are your end goal, right?).
Let’s take a look at some eCommerce SEO best practices:
- Each product should have a unique and keyword-optimized meta title and description.
- Products should not be listed twice and should have unique URLs.
- Categories should not be included in the URLs (you want the products to be visible across multiple filters/facets). Keep the product page URLs clean and short.
- Each product should be listed in at least one indexable path. As shown before, you don’t want to index all the instances where your products appear (e.g. filter pages), that’s why you’ll tell search engines not to index them. However, make sure you have each product listed in an indexable path.
- Out of Stock product pages can be left indexable if temporary, but make sure to recommend related products until the stock is back. This way, you won’t lose the traffic.
If the product will remain permanently out of stock, you can use a 301 redirect to the next closest relevant page (or even to the product’s category page), to not spill the link equity collected on the initial out-of-stock product page.
- Add reviews on product pages
-
Category Pages
- Each category page should have a unique meta title and description
- As already outlined, you don’t want to index filter pages (so as to avoid duplicate content and crawling budget issues). However, you need to index the main category pages that are part of your website’s main navigation.
- Each category page should target a keyword. Being indexable, you want to rank with these pages.
3. Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to all the external sources that can influence your eCommerce website’s ranking in SERPs. Essentially, after you have optimized your website, you need to spread the word about it.
Note that off-page SEO goes beyond backlinks. Although these are still the most important signal, authority and trustworthiness can be signaled by other sources as well (such as unlinked mentions, branded searches, reviews on dedicated websites, etc.).
However, for your eCommerce SEO audit, you want to start with the following off-page action items:
-
Backlinks
To this day, backlinks are still one of the most important ranking signals considered by search engines.
You know how customers tend to trust third-party reviews and word-of-mouth more than the company itself? That’s exactly how the search engines behave too.
Backlinks are external links from other websites that link to your website. They have a prominent role in ranking because they pass the link authority to your website. That’s why getting backlinks from reputable websites with high authority in your industry should be a priority. However, if these links have a “nofollow” attribute attached to them, the link equity will not be passed on to your website. Although there’s not much you can do about this, even an unlinked mention can build up to your authority. However, your focus will still be to get “dofollow” backlinks.
The process of gaining backlinks takes time, but it’s worth it. There are many proactive link-building strategies you can use, and broken link strategy, guest posting, and participating in roundups/interviews are just some of them.
At the end of the day, if you create quality content (such as original research), websites will naturally link to it.
A best practice would be to keep track of your brand mentions. In case some negative comments arise, you can join the conversation and protect your authority. In your SEO audit, having an overview of the quality of the backlinks you have is important in establishing a benchmark to compare against your results following, let’s say, a link-building effort.
-
Social media engagement
Social media is separate from search engines, and does not have a direct say in your ranking.
However, social media contributes tremendously to your reputation, authority, visibility, i.e. all the elements that off-page SEO is looking to improve.
4. Content Audit
Content auditing is another essential part of your website audit, if not the most important. In the end, your whole website is built around content.
A content audit helps determine if your current content efforts are working towards the established goals you set. It also provides the necessary insights so you can fine-tune your content strategy for better performance.
A content audit should help you identify your best-performing content pieces, those topics that are preferred by your audience (along with the ones that are wasting your resources). A content audit can also unveil content gaps (maybe there are some topics that your audience resonates with, but you haven’t covered yet).
Take your audit a step further by assessing your competition’s content as well. You can understand what keywords they are ranking for, which of their content performs particularly well, as well as potential gaps that you can fill.
There are some characteristics that your content should mark off the checklist:
- Uniqueness – avoid duplicate content issues and thin-content (i.e. low-quality content). One way to solve this issue when you cannot simply avoid it (as in the case of filter pages) is to use the re=canonical tag, as we pointed out. However, the most effective solution to duplicate/thin content is to create unique and original When writing your product description for example, you can try to answer all the questions the users could have relative to it. Adding other pieces of content like photos/videos and reviews is also good.
- Usefulness – informative and useful content is designed for your buyer personas, and based on the stage in the buyer journey that visitors find themselves in. That is, a prospect finding themselves in the interest stage needs a different type of content than a long-term client. You may also want to group your pieces around topic clusters, so users can easily find what they are looking for without having to leave the website. Your content should serve the interests of visitors, not of search engines.
- Accuracy – it’s a no-brainer, but your content should be error-free, both in terms of grammar/spelling and of facts/statistics used to back-up your assertions.
- Freshness – to keep your content qualitative and relevant, you’ll want to update and make supplementary additions to it every now and then.
- SEO–friendly structure – this refers to making your content easily readable by both users and search engines. This is what on-page SEO is about, as we discussed above. In addition, you may want to consider optimizing your content for SERP’s features like snippets/reviews/FAQs. This can be achieved by including structured data in the HTML code.
- The best of the best – there’s a saying among SEOs that content should be crafted as if there is a real chance for it to be better than the pieces that are already ranking for the targeted keyword. You want to at least start with this mindset when creating content.
Now, you’ll work with some extensive spreadsheets in your content audit. It will take some time, but it’s an essential activity in your website audit. That’s how you can keep your content relevant and qualitative, as both search engines and users want.
E-A-T
The end goal of your strategy is to have E-A-T content.
Following Google’s June 2019 update, more importance was placed on E-A-T when ranking pages.
Don’t worry, this is not another daunting task to cut off the checklist. In fact, all that we’ve discussed until now leads to this end goal. Your overall website should demonstrate:
- Expertise – as a provider of a particular product, you most likely have a skilled team that possesses subject-matter expertise in your field. You certainly need to emphasize this, as Google will evaluate author’s E-A-T, not only that of the website. If you have a blog, author bios can help tremendously. Expertise also amounts to complying with the checklist we went through earlier – delivering unique, useful, accurate, and fresh content that solves your audience’s queries.
- Authority – this is all about off-page SEO. All the external links you gain from industry peers, brand mentions, social shares, etc. contribute to building your authority in the field.
- Trustworthiness – this is fostered in several ways. Essentially, you want to be transparent and provide a secure experience to your customers. HTTPs, privacy policies, refund and return policies, or contact details can contribute to build a trustworthy reputation. Oh, and since we’re at this point, managing your online reputation is also part of the story – you can restore trustworthiness by managing negative reviews you get on review websites.
5. User experience
Last, but not least, is user experience, because this is also a ranking factor. Google evaluates a website’s usability when ranking results.
Here are some items that you need to keep in mind for this part of your website audit:
-
Mobile friendliness
Since 2019, Google has mainly been using the mobile version of the website for indexing and ranking. It goes without saying that mobile-friendly websites will be prioritized in SERPs.
In addition, by 2021, it is forecast that mobile eCommerce sales will account for more than half of all eCommerce sales. Mobile commerce is on the rise.

These two arguments alone should be enough to justify why you need to go mobile.
-
Site and page speed
Neither users, nor search engines, like slow websites. In terms of user experience, lengthy load times can increase bounce rates and cart abandonment, and, ultimately, can lower your conversion rates. In terms of SEO, your website will certainly rank lower.
As part of your audit, make sure you learn what elements are slowing down your website and optimize them for improved speed performance.
-
How are users using your internal site search?
Your internal site search is a great resource, as it provides you with first-hand data about the way users interact with your website. Google Analytics allows you to track the keywords introduced by users in your search bar, and you can even use some of those in your keyword research.
You can also discover the most searched items in your store (and leverage those in campaigns), or identify topics that users are most interested in. If users continue to stay on your website after performing a search, then your content is satisfying their needs. Otherwise, you need to work on it.
All in all, a search function improves user experience because users can effortlessly navigate your website. It also provides you with valuable insights to implement and further optimize your on-page SEO.
-
Bounce rate, average time on page, and exit pages
Google Analytics provides useful metrics that will help you determine how users are interacting with your website.
For eCommerce websites, a lower bounce rate is ideal. eCommerce sites tend to have between 20% to 45% bounce rate. You want to keep them hooked by your site, to navigate from page to page, and finally, to convert. Improving your bounce rate is a matter of optimizations (including content and internal linking)
Average time spent on page goes hand-in-hand with the bounce rate. It’s part of keeping users hooked by your website. The longer they spend consuming your content, the higher the chance they will convert. But again, having a higher average time spent on the page depends on the content quality.
Identifying pages that have a very high exit rate is also part of the optimization process. In fact, it’s another way of identifying problematic pages, in a very timely manner. You can then check for all the aspects we’ve discussed so far. Is the page technically optimized? How are the on-page elements, particularly the content?
Best SEO Tools to Audit Your eCommerce Site
We’ve mentioned some tools that can help you tremendously in your eCommerce SEO audit.
Now, it’s time to take a quick dive into the best tools which can automate some of the previously discussed tasks for you.
SEMrush
SEMrush caters to multiple search engine marketing (SEM) needs, hence its name.
This tool is particularly helpful for on- and off-page SEO, including:
- Keyword research (you can see for which keywords you are ranking, as well as discover new, related keywords)
- Backlinks (to monitor them)
- Competitor analysis (SEMrush is great as it allows you to retrieve all the aforementioned data for competing domains, too)
Ahrefs

Ahrefs is widely recognized for its Site Audit function, helping more on the technical side of SEO. You can configure it to crawl your website and it can return a bunch of technical issues.
Ahrefs is also widely used for backlinks. Having an impressive index, this tool allows users to easily identify what sites are linking to each other, what sites are linking to competitors but not to them, and more. This enables you to efficiently identify link opportunities.
Google Search Console

Google Search Console is a webmaster tool. It will prove particularly useful in identifying and fixing technical issues (you can use it to submit your sitemap, identify structured data issues, errors, and more).
PageSpeed Insights
Provided by Google, this tool returns information about the speed of any web page (on both mobile and desktop), as well as suggestions to improve loading time.
Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is dedicated to technical SEO, as it can crawl your website and return all kinds of issues, including broken links, duplicate content, faulty metas, and much more.
Majestic SEO
Majestic SEO is a tool exclusively focused on link analysis. Their reports provide detailed metrics about the links on a domain, such as Trust Flow, Topical Trust, External Links, Crawled and Indexed URLs, and much more.
WooRank
WooRank provides an array of data to help in technical and on- and off-page SEO.
From crawling and indexing issues, to performance issues and keywords and content, this tool comes in handy for keeping your website optimized.
Bonus – For a complete list of SEO tools to improve your rankings, check out this article.
Conclusion
An eCommerce site audit might seem like a daunting task. Apart from the typical issues encountered in any SEO audit, eCommerce websites bring their own layer of complexity to the job, with all those product and dynamic pages we’ve talked about.
But fear not, once you systematically start to audit your website, you’ll see why this task is not that daunting. It only takes time, and with all the SEO tools at hand, even the time spent on it is minimized. Make sure you focus on the plethora of elements that you’ll audit. Keep it systematic.
As you’ve already seen, a lot of SEO optimizations come down to making your website trustworthy, not for the search engines, but for your potential customers. As an eCommerce business, having a reliable website is even more important.
And a last piece of advice – be patient. SEO results will gain traction in time.
Good luck on your SEO audit!